

4.25.1 Controlling the visibility of forwarded ports.4.24.2 X authority file for local display.4.23.1 ‘Don't allocate a pseudo-terminal’.4.22.2 Preference order for GSSAPI libraries.4.22.1 ‘Allow GSSAPI credential delegation’.4.21.8 ‘Private key file for authentication’.4.21.7 ‘Allow attempted changes of username in SSH-2’.4.21.5 ‘Attempt keyboard-interactive authentication’.4.21.4 ‘Attempt TIS or CryptoCard authentication’.4.21.3 ‘Attempt authentication using Pageant’.4.21.2 ‘Display pre-authentication banner’.4.21.1 ‘Bypass authentication entirely’.4.19.1 Key exchange algorithm selection.4.18.5 Sharing an SSH connection between PuTTY tools.4.18.4 ‘Preferred SSH protocol version’.4.18.2 ‘Don't start a shell or command at all’.4.18.1 Executing a specific command on the server.4.16.4 ‘Return key sends Telnet New Line instead of ^M’.4.16.3 ‘Keyboard sends Telnet special commands’.4.16.2 Passive and active Telnet negotiation modes.4.16.1 ‘Handling of OLD_ENVIRON ambiguity’.4.15.5 Specifying the Telnet or Local proxy command.4.15.3 Name resolution when using a proxy.4.15.2 Excluding parts of the network from proxying.4.14.5 Setting environment variables on the server.4.13.1 Using keepalives to prevent disconnection.4.12.6 Adjusting the colours in the terminal window.4.12.4 ‘Attempt to use logical palettes’.4.12.3 ‘Indicate bolded text by changing.’.4.12.2 ‘Allow terminal to use xterm 256-colour mode’.4.12.1 ‘Allow terminal to specify ANSI colours’.4.11.5 Configuring word-by-word selection.4.11.3 ‘Shift overrides application's use of mouse’.4.11.2 Changing the actions of the mouse buttons.4.10.5 Controlling copy and paste of line drawing characters.4.10.4 Controlling display of line-drawing characters.4.10.3 ‘Caps Lock acts as Cyrillic switch’.4.10.2 ‘Treat CJK ambiguous characters as wide’.4.10.1 Controlling character set translation.4.9.5 ‘System menu appears on Alt alone’.4.9.4 ‘System menu appears on ALT-Space’.4.8.3 ‘Hide mouse pointer when typing in window’.4.8.2 Controlling the font used in the terminal window.4.8.1 Controlling the appearance of the cursor.4.7.4 ‘Push erased text into scrollback’.4.7.2 What to do when the window is resized.4.7.1 Setting the size of the PuTTY window.4.6.10 Disabling bidirectional text display.4.6.8 Disabling remote character set configuration.4.6.6 Response to remote window title querying.4.6.5 Disabling remote window title changing.4.6.4 Disabling switching to the alternate screen.4.6.3 Disabling remote terminal resizing.4.6.2 Disabling xterm-style mouse reporting.4.6.1 Disabling application keypad and cursor keys.4.5.3 ‘Control the bell overload behaviour’.4.5.2 ‘Taskbar/caption indication on bell’.4.4.8 ‘Control-Alt is different from AltGr’.4.4.5 Controlling Application Keypad mode.4.4.4 Controlling Application Cursor Keys mode.4.4.3 Changing the action of the function keys and keypad.

4.4.2 Changing the action of the Home and End keys.4.4.1 Changing the action of the Backspace key.4.3.5 ‘Use background colour to erase screen’.
#ANSI ESCAPE SEQUENCES FUNCTION KEYS SERIES#
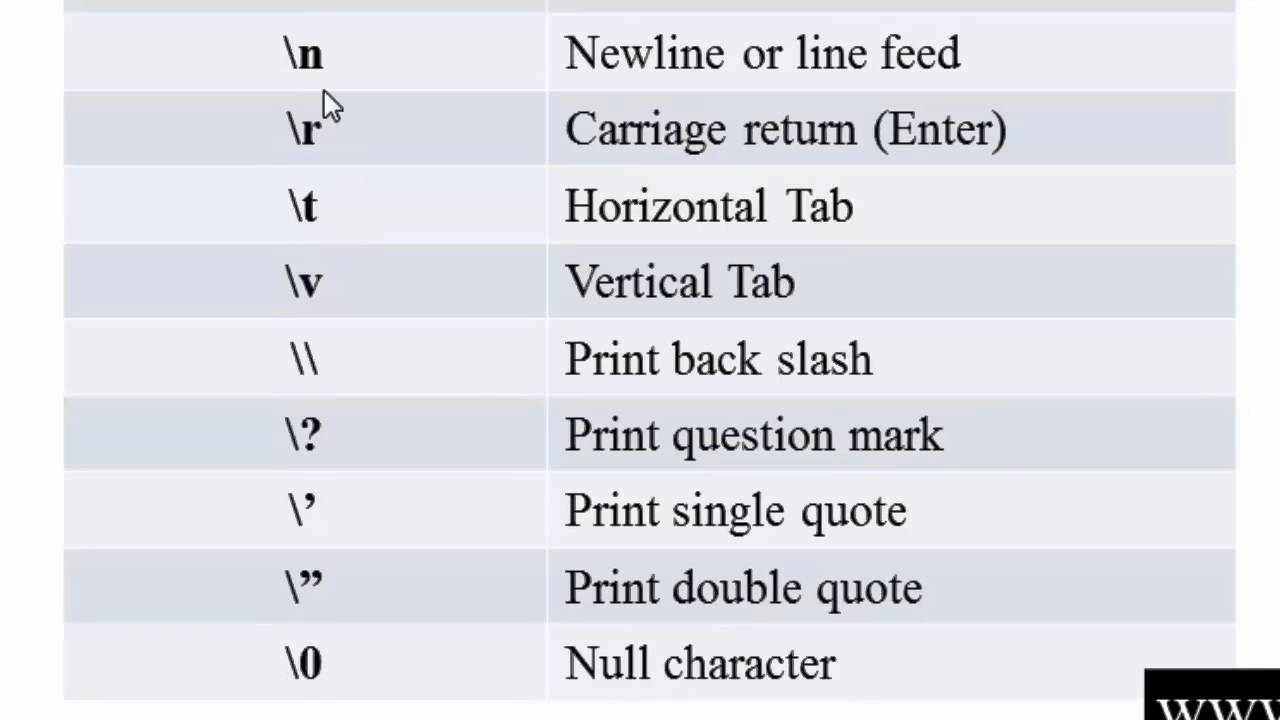
A sequence is just a set of two or more characters and an escape where the sequence begins with a backslash (\\) and other characters in the set follow that backslash.Īn escape sequence is a sequence of characters that, when used inside a character or string, does not represent itself but is converted into another character or series of characters. So here comes the role of escape sequences.įirstly, understand sequences. Suppose you have the string containing a double backslash (\\\\), and you want to print the string with a double backslash, but it is impossible to print it directly. Introduction to Escape Sequence in Python This character serves as an escape sequence initiator, and every character (one or more) following it is considered an escape sequence. In the escape sequence, a character is preceded by a backslash (\) followed by the character you want to represent for the new line. An escape sequence is a sequence of characters that, when used inside a character or string, does not represent itself but is converted into another character or series of characters that may be difficult or impossible to express directly, like newline (\n), tab (\t), and so on.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
